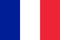
Joint painThe fingers are an indispensable sign of any joint pathology in which the structural components of these joints are damaged.First of all, pain in the area of these joints may be associated with various autoimmune diseases (Systemic red shine, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, etc.) In which immune factors cause damage to their own joint tissues.
The next main reason that can startpainIn the fingertips, there may be injuries (bruises, displacements, bone fractures, ligaments).Pain in these joints can also be caused by degenerative changes that occur in their joint tissues.This can usually be observed with osteoarthritis.
Hand joint anatomy
All joints of the hand are usual to be divided into the following groups:
- joint of the wrist;
- Pulse joints;
- Carpal standard joints;
- interpecial joints;
- Phalanx Parlémal's together;
- Interfalanx together.
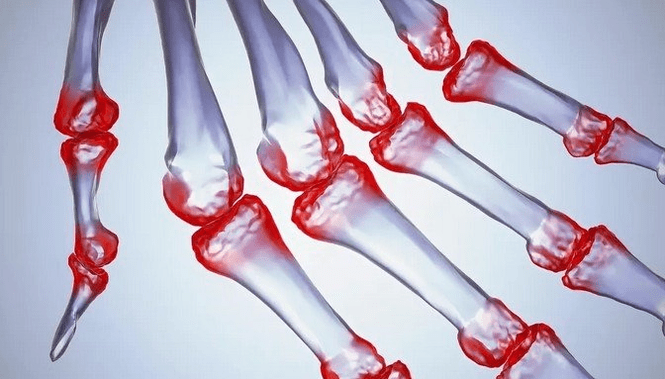
The articulation of the pulse
The articulation of the pulse is formed by the bones of the proximal bones (superior) several pulses (TRIEDRAL, SEMI -LUUA, ESCAFACE BONES) and distal areas of radiation and elbow bones.The elbow bone is not directly connected to the bones of the wrist, but with the help of distal (Lower) The articular disk.This structure separates the cavity from the articulation from the distal cavity pulse (Lower) The articulation of tiles.
Pulse joints
Pulse joints are represented by three types of joints.The first form includes the joints located between the upper bones (scaphy, semi -lua, triedral, pea -shaped) or the lower line (in the shape of hook, head, trapezoidal, bone capture).These joints are called interchangen joints.In the second type, the intermediate writing board is classified.This joint has a form in the form of s and is formed due to the connection of the upper and lower line bones of the wrist.The third type includes the pea bone joint.Through this articulation, the triedral bone is connected to the pea bone.
Capacen-Peenal Articulations
Carpo panel joints connect the bones of the pulses and metacarpal bones.These joints are formed by contacting the proximal ends (land) Metacarp bones and distal sections of the carpal bones belonging to the second line.Carpal standard joints include two main joints.The first is the thumb articulation.It is formed by connecting the first bone bone with bone capture.
The second articulation is the common articulation of the carpal to the rest of the carpo-prypyna compounds between the second, third, fourth, fifth metacarpal bones and trapezoidal bones, head and partially a bone cheating section.The carpal standard joint of the thumb is separated from the total joint of carpal patterns.Due to which more active movements are possible in it, compared to the rest of the carpal paths (which are included in the General Board of Carpo Camo) which are considered sedentary.The carpal panel joints are strengthened by strong joint capsules as well as ligaments (Ligaments Back and Palmar).
Interprets articulations
The side surfaces of the bones of the second, third, fourth and fifth metacarp, when contacted by each other, form interprex joints.These joints have separate joint capsules, which are approaching the capsules of the carpal path joints, are connected to them.In addition to the capsules, these joints have a ligament apparatus represented by metacarpal ligaments between scenes, as well as the rear ligaments and paired Palmar.Interpener joints are attributed to the sedentary joints of the hand, since the joint surfaces of the bones that form these joints have a flat form.
Parleen-phalanx joints
Parleus-Phalanx joints are composed between distal (lower) With the ends of the metacarpal and proximal bones (superior) Areas of the first phalanxes of the fingers.Each finger of the upper limb has its own metacarpalis joint.Thus, there are five metacarpal forgery joints in each hand.
Interfalanx joints
Interpofalanx joints are formed by the combination of neighboring phalanxes of each of the fingers.Big (first) The finger has only one interfailed articulation, as this finger has only two speech (proximal and distal).The rest of the fingers of each hand has two joints of interphalândia.
The first of them is located between the first (proximal) and the second (average) fingers and called proximal phalanges (superior) Interfalang Board.The second form the connection between the average (second) and the last (distal) Phalanges of the fingers.The second interphalangeal joints are called distal intervened joints.Inter -Falanx joints are strengthened with collateral and palm ligaments.These joints belong to the block joints, whose movements are possible only around the front plane (Fighting and bending).
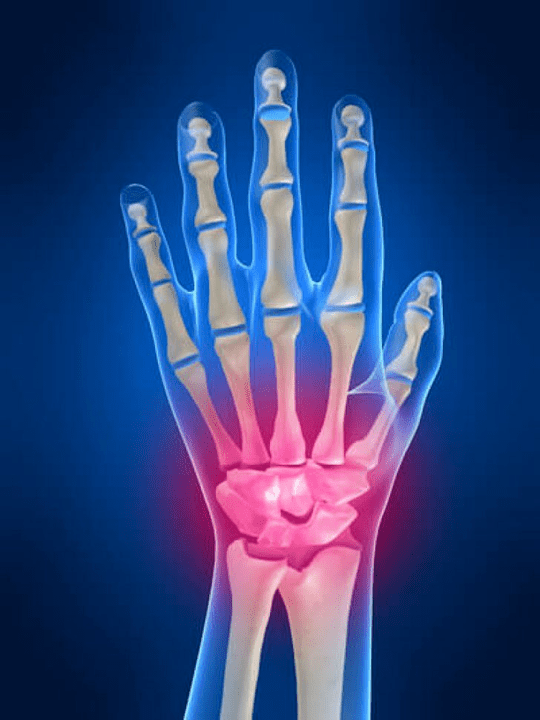
What structures can be inflamed in the joints of the hands?
Inflammation is a typical pathological process characteristic of tissues and organs that have been damaged for any reason.It is worth remembering that, in most cases, all diseases (For example, gout, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.) or trauma that damages the joints of the hands to one degree or another, affect not only the articulate, but also the perioster (nerves, muscles, tendons, subcutaneous fat, skin) Structures.
The following joint structures may be inflamed in the joints of the hands:
- joint cartilage;
- Squeezer bone tissue;
- joint capsule;
- Joint ligaments.
The causes of pain in the joints of the hand and fingers
The main participation between the reasons that cause pain in the joint and fingertips is occupied by mechanical injuries (Fractures, displacements, bruises, etc.) and systemic autoimmune diseases (Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, etc.).In addition to these causes, pain in hand joints can cause diseases associated with metabolic disorders (For example, gout, osteoarthritis).
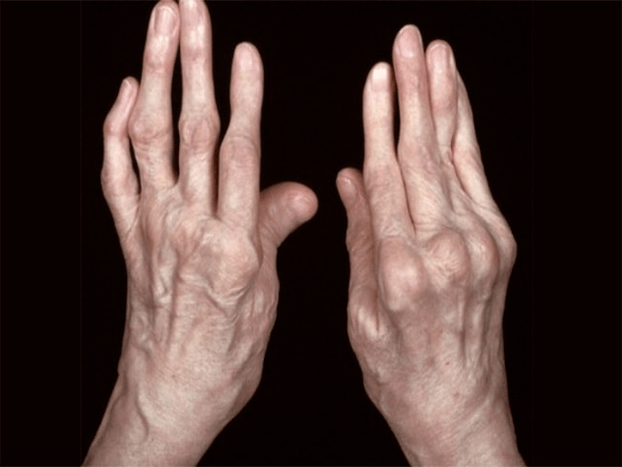
There are the following main causes that cause pain in the joints of the hand and fingers:
- hurt the hand and fingers;
- Brush bone fracture;
- brush displacements;
- Injury of the ligaments of the hand;
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Kinbek's disease;
- reactive arthritis;
- drop;
- psoriatic arthritis;
- SYNOVITE;
- osteoarthritis;
- Red lupus of the system.
Brush and finger
A bruise is one of the types of closed lesions, in which there is damage to soft tissues (muscles, tendons, nerves, skin) And there are no wounds where the main action of the traumatic factor was directed.Soft tissue bruises of the hand and fingers are very rarely found in isolation (separately) from bruises of the joints of the hand and fingers.Therefore, with this type of injury, mixed symptoms are found, indicating damage to the joints of the hand and the periarticular injury (peri -human) Tissues.Brush and fingertips are usually found when falling into the hand, damage it with a blunt object, with its compression or pinch.
Often cystic bruises lead to damage to the main medium, radial and elbow nerves (that innervate the area of the hand and fingers), which immediately manifests the loss of skin sensitivity and, in some cases, even by the disappearance of finger motor functions.
The inflammatory edema of joint and peri -human structures develops as a result of the expansion of numerous vessels that are blood supplies.This edema is one of the reactions of inflammation, which occurs in response to damage to tissues during bruises.
A fracture of the brush bones
Often the cause of pain in the hand joints can be several fractures of their bones, as these bones are directly recorded in the formation of joint surfaces.Depending on the anatomical position of the damaged bone, all fractures are divided into three main groups.The first group includes wrist bone fractures.The second includes tubular metacarpal bone fractures.The third group includes finger phalanges bone fractures.
The most frequent places of damage in the carpal zone of the brush are the semi -lua and scaphoid bones.A fracture of these bones occurs during the drops in the brush and is accompanied by pain in the tist and medium wrist joints area.Pain syndrome can also be observed in places of anatomical location of these bones.
The most frequent fracture of the ends of metacarpal bones is a fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone (the one who is stuck to the phalanxes of the thumb bones).With this lesion, edema and pain appear in the base zone of the first metatarsal bone, as well as in the part of the carpal standard joint, which directly adjacent to it.The thumb of this fracture is shortened, folded and led to the palm of his hand.Your movements are limited.
Brush phalanx fractures are accompanied by deformation, a decrease in fingertips, the loss of their function, acute pain and swelling in their interfalanx joints and peri -human tissues.With phalanx fractures of the fingers with a displacement of bone fragments, palpation (in palpation) You can identify their bulging on the palmar surface of the brush and, on the back, on the contrary, a hole or isolation.These fragments are usually mobile, near them, you can detect subcutaneous bleeding (Hematomas).
Brush lubrication
Dislocation is a pathological condition in which the areas of bones that form any articulation go beyond their anatomical limits, which, therefore, manifest themselves by a complete or partial loss of the function of this articulation.In addition to the impaired joint function during displacements, severe pain in the affected joint, swelling and local temperature increase are also found.During brush dislocations, the appearance of swelling is explained not only by the presence of inflammation in damaged peri -Human tissues, as well as by the structures of the joint, but also with a protrusion of emanated bone joint.
The most frequent types of brush dislocations
| The name of dislocation | The displacement mechanism | Which articulation is surprised? |
| True brush displacement | The joint surfaces of the wrist bones are shifted to the articular surface of the radial bone towards the palm of the hand or on the back of the hand. |
|
| Perilunar dislocation | The bones of the wrist and the rest of the brush are displaced in relation to the middle -dia and radial bone in the back of the brush. |
|
| Bone dislocation | At the same time, the scaphoid bone displays the dislocation on the side of the parallel radiation (On the same plane) For bones near the wrist.Sometimes you can change on the palmar side, that is, to change to the palm of bone swam, with less frequently on the same side of the trapezoidal bone. |
|
| Luxation of the semi -lua | There is a slide of the sock -way towards the palm, so that the space in place of this bone remains not busy.It is gradually occupied by the bone of the head, penetrating here from the second row of the bone of the wrist.This dislocation is a complication of perilunar dislocation self -regulation. |
|
| First Metacarpo bone dislocation | The joint surface of the base of the first metacarpal bone is displaced in relation to the joint surface of bone capture on the side of the radiation,proximal) and on the same plane with the bones of the wrist.Thus, the thumb is pulled a little back and toward the wrist joint. |
|
| Finge phalanges dislocation | There are dislocations of the fingertips in the metacarpofolangic joints and in the interfalanx joints.In the first, the proximal phalanx surface of the fingers (Along with the whole finger) changes in relation to the articular surface of the metacarpal bones.With the second, there is a displacement between the bones of the phalanges of the finger itself.Generally, there are dislocations in the back and palm trees of the finger phalanges. |
|
Damage to Ligaments of the Hand
Ligament injury, along with brush bruises, is attributed to closed traumatic damage.This pathology is mainly found with excessive hand extension, fingers in any direction.The main types of brush group injuries are stretching and rupture.With stretching in the damage zone, a slight tension and partial rupture of connective tissue fibers is observed.With the rupture of ligaments, the entire ligament is divided into two endless ends.
The following main types of brush ligaments are distinguished:
- Radial collateral ligament rupture of the pulse;
- collateral ligament rupture of the wrist elbow;
- Rupture of interception ligaments;
- Rupture of lateral ligaments of metacarpal falsification joints;
- Rupture of lateral ligaments of the interfalang joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease in which the human immune system damages the body's own tissues.In other words, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune pathology.This disease is also systemic, since many tissues are affected with it (muscles, joints, pots, etc.) and organs (Heart, kidneys, lungs, etc.) In the body.
Despite the fact that rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease under it, to a greater extent, the joints suffer, while the injury of other tissues and organs is in the background.With this disease, almost all types of brush joints can be affected (Wristwalls, Carpal Pathas, Metacarpal-Phalanx, Inter-Phalanx Joints).The lesion is usually symmetrical (those ones.The same joints are affected) In both hands, accompanied by swelling, pain in damaged joints.In the morning, during bed lifting, there is some stiffness in the affected joints, which can last about 1 hour and then disappear without a trace.
Often with rheumatic arthritis near the affected joints of the brush (More often, piano-phalanx, inter-Falanx joints) Rheumatoid nodules appear.They are a rounded formation located under the skin.In the brush, these formations appear more often on the back.In palpation, they are dense, inactive, painless.Their number may vary.
Kinbek's disease
Kinbek's disease is a pathology in which a semi -brush tinnitus bone is affected.The disease develops as a result of long -term physical physical overload of the palms.Usually occurs in experts in construction professions - implase, bricklayer, cabinetmakers, etc.Excessive physical activity of the palms of the hands of the hands more often this bone, since it occupies the central position in the wrist joint.Most of the time, during Kinbek disease, the brush of a hand is affected and, as a rule, the mainThe right hand is damaged, the left hand is damaged).
Reactive arthritis
Reactive arthritis is a pathology of immunopathological genesis, in which its own immune system attacks various joints in the body, which is why autoimmune inflammation develops in them.Unlike other autoimmune diseases (For example, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, in the occurrence of which an infectious origin is assumed) In reactive arthritis, a clear relationship between the infection is tracked (and, in particular, intestinal or urogenital) and the development of joint lesions.
Also, with this pathology, lymph nodes can increase and fever appears.When reactive arthritis transitions to a chronic form, over time, patients may indicate signs of kidney disease, heart and muscle atrophy, bursitis can occur (Inflammation of the sinker bags), having vaginites (Tendon vagina inflammation) and others.
Drop
Gout is a disease based on the development of the accumulation of uric acid in the body and its testimony in the form of salts in the joints.Urral acid is the final product of the metabolic of the bases of purine and pyrimidine.They serve as the basis for the construction of DNA and RNA molecules, some energy formations (Adenosine triphosphate, adenosine monophosphate, etc.) and vitamins.
Drop pain occurs mainly in small joints from the lower and upper ends.In addition, in 50% of all clinical cases, the disease begins with the first positive leg joint.In the hands, as a rule, the interfailed joints of the fingers are affected, less frequently - radiant joints.The drop usually damages one or more joints on a limb, sometimes the joints of other members are involved in the inflammatory process.
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a pathology in which several joints are inflamed against the bottom of psoriasis.The development of psoriasis is based on violation of the interaction between immune cells and skin cells as a result of the body (And especially on the skin) There are autoimmune reactions that cause inflammation.
Synovitis
Synovitis is an inflammation of the synovial shell of the joints, accompanied by damage to its tissues and the accumulation of pathological fluid in the affected joints.Synovitis is not a separate disease, but serves as a complication of other diseases.It can occur with endocrine, allergic, infectious and autoimmune pathologies, brushes, etc.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a disease in which there is a violation of the normal tissue formation processes of the cartilage in various joints.These processes are violated under the influence of certain external and internal predisposing factors.They can be constant joint injuries, prolonged physical activity (At work, in everyday life, during the sport), heredity, other joint diseases, etc.
The articulations of the fingers are painful with this pathology, because in periarticular (peri -human) Tissues occur inflammation, nerves are affected.One feature of osteoarthritis is the connection of pain to physical activity.Joint pain appears mainly in and/or after a heavy physical overload and disappears at rest or after rest.
Red system lupus
A systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune pathology, in which in the human body there is a production of an immune system of autoimmune antibodies, attacking various cell and tissue structures.In particular, with it, the production of anti -core antibodies as soon as they damage cellular nuclei and DNA and RNA molecules are observed.With a red lupus, various tissues and organs are affected - leather, pots, heart, pleura, pericardium, kidneys, joints, etc.
Red lupus of the system is constantly associated with other extra signs - intact - weakness, weight loss, fever (Improving body temperature).However, special symptoms are of greater importance, without which the diagnosis of red lupus is not made.These special signs are photodermatitis (Skin inflammation under the influence of sunlight), discourse rash (The appearance in the neck skin, red paper chest), Lupoid Butterfly (The appearance of red spots on the skin near the nose), erosion in the oral cavity, kidney damage (Glomerulonephritis), serosites (Serous membrane inflammation) and others.
Diagnosis of the causes of pain
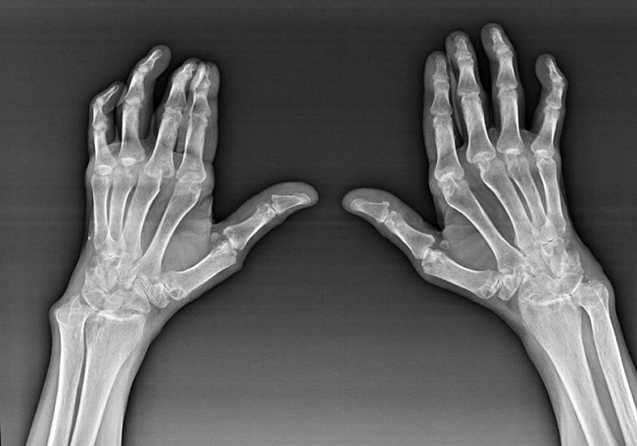
Hands of pain in the joints of the hand are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of the causes of pain, especially a traumatologist and a doctor of A. to diagnose these reasons, these doctors use mainly clinicals (Anamnesis collection, external inspection, palpation, etc.), radial (Radiography, computed tomography) and laboratory (General blood test, biochemical blood test, etc.) Research methods.
Depending on the cause of pain in the hand joints, all diagnoses can be divided into the following sections:
- Diagnosis of traumatic brush injuries (bruises, displacements, fractures, ligaments);
- Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis;
- Diagnosis of Kinbek's disease;
- Diagnosis of reactive arthritis;
- Diagnosis of gout;
- Diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis;
- Synovitis diagnosis;
- Osteoarthritis diagnosis;
- Diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus.
Diagnosis of traumatic brush injuries
When brush lesions, you should consult a traumatologist.The main diagnostic methods that are used in medical practice to identify traumatic damage to the brush (fractures, displacements, ligaments, bruises), are an external examination, anamnesis, research radiation methods (Radiography, computed tomography).
Anamnestic data collection allows the doctor to identify incidents that have led or may lead to a brush injury.The history of anamnesis is also used to clarify the symptoms that bother the patient.During an external examination in the brush, it is possible to detect swelling, bruises, its deformation, limitation of joint mobility.With the help of palpation, the doctor reveals the presence of pain, violation of the anatomical form of the joint, damage to ligaments.Research radiation methods (Radiography, computed tomography) They allow you to confirm the diagnosis, because during use, mechanical damage to anatomical brush formations are clearly visible.
Treatment of pathologies that cause inflammation of the joints of the hand

For the treatment of causes of pain in the joint and fingers, doctors, first and foremost, prescribe a variety of medications (Anti -inflammatory, painkillers, anti -rhevets, etc.).In some cases, they combine the use of these products with physiotherapeutic procedures.Traumatic damage to brush is most often surgically treated or applied to the affected upper member of the plaster dressing.
To relieve pain and relieve inflammation, the first help may be the use of an external NSAine.The drug selectively blocks COO-2 and acts directly on the source of pain.It is quickly absorbed thanks to a special texture, leaves no traces of clothing, has a pleasant smell.
Depending on the pathology that causes inflammation in the joints of the hand, all treatment can be divided into the following parts:
- Treatment of traumatic brush injuries (bruises, displacements, fractures, ligaments);
- Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis;
- Kinbek disease treatment;
- reactive arthritis treatment;
- Got treatment;
- Treatment of psoriatic arthritis;
- Synovitis treatment;
- osteoarthritis treatment;
- Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.